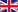
Natürlich habe ich das sprichwörtliche Grauen schon weit vor dem Aufgang der Sonne bemerkt. Und natürlich hätte ich mich gar nicht erst auf den Weg machen müssen, nachdem der Blick vom Balkon um 3 Uhr nachts bereits nichts gutes verhieß:
Warum ich trotzdem losgezogen bin? Weil es schon seit einer Woche nicht anders aussah und ich die Schnauze voll hatte. Weil mein Fotospot leicht erhöht liegt, vielleicht könnte ja ich über den Nebel hinwegfotografieren, aus dem optimalerweise nur die Kirchturmspitzen herausragen und es würde sogar richtig gut aussehen? Weil der Nebel sich bis zum Sonnenaufgang in zwei Stunden vielleicht eh wieder verzogen haben würde? Weil ich ja immerhin auch Sterne sehen konnte, wenn ich senkrecht nach oben geschaut habe? Wie sich herausstellen wird, waren meine Hoffnungen unbegründet, fast naiv. Als ich am Zielort ankomme, scheint sich das ganze noch verschlimmert zu haben, man sieht gar nichts.
Um dieses Ärgernis zumindest besser zu verstehen, es beim nächsten mal besser abschätzen und vielleicht ja sogar gestalterisch auch mal ausnutzen und vorhersagen zu können, folgt nun also die theoretische Auseinandersetzung:
Was ist Morgennebel?
Morgennebel ist nichts anderes, als eine Wolke in Bodenhöhe. Tausende winziger Wassertröpfchen schweben in der Luft und rauben so die Sicht.
Wann kommt Morgennebel?
Die kurze Antwort: besonders, wenn es am Tag zuvor warm war und eine sogenannte Hochdruckwetterlage besteht, also vor allem bei schwülem Wetter. Da gibt es meist keine oder nur wenige Wolken und wenn es dann Nacht wird, strahlt der Erdboden seine Wärme zurück ins Weltall. Dabei kühlen sich die bodennahen Luftschichten ab. Kalte Luft kann leider weniger Wasserdampf aufnehmen als warme Luft, d.h. ihr Taupunkt wird schneller erreicht, die Feuchtigkeit der Luft beträgt also 100% und der Wasserdampf kondensiert als flüssiges Wasser aus. Das sind dann die Tröpfchen, die den sichtbaren Nebel am nächsten Morgen bzw. schon in der Nacht bilden und mich die letzte Woche jedes mal den Sonnenaufgang gekostet haben.
Wann verschwindet er wieder?
Meine persönliche Antwort: leider nicht so schnell wie ich gerne hätte! Auch am heutigen Morgen konnte ich zwar erahnen, dass da hinterm Grau irgendwo die Sonne aufgeht, aber gesehen hab ich das nicht:
Wenn man sich mal bewusst macht, was es braucht um den Nebel wieder verschwinden zu lassen, wundert einen das aber auch nicht. Natürlich muss die kühle Luft wieder erwärmt werden, um mehr Wasserdampf aufnehmen zu können, so dass die Tröpfchen wieder verschwinden. Da der Boden seine Wärme über Nacht abgestrahlt hat, braucht es dafür die Sonne, und zwar viel davon! Der Nebel ist leider ein guter Reflektor und gibt etwa 90% der Sonnenstrahlung direkt wieder zurück. Die restlichen 10% müssen es also reißen und den Boden und die bodennahen Luftschichten wieder ausreichend stark erwärmen. Die logische Konsequenz ist also: bevor die Sonne nicht aufgeht, verschwindet auch der Nebel nicht! Und selbst dann braucht es erstmal noch etwas Zeit.
Tja, dieses Wissen hätte mich heute ein paar Stunden länger schlafen lassen können. Wieder was gelernt!
P.S.: Es gibt allerdings noch einen Joker: den Wind. Wenn man Glück hat und dieser trockene Luft heranbläst, sinkt die durchschnittliche Luftfeuchtigkeit und der Nebel kann sich relativ rasch auflösen. Heute war es leider absolut windstill.