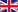
Das Bild
Bevor wir zur Thematik des Bilderklaus kommen, ein paar Worte zum Gegenstand an sich. Das Bild entstand bereits 2013 in Australien. Zu sehen ist ein Teil der 12 Apostel, eine bekannte Küstenformation und zugleich Touristenattraktion an der Great Ocean Road, einer bekannten 243km langen Straße entlang der Südküste des Kontinents im Bundesstaat Victoria. Das Motiv findet man zuhauf im Netz, es ist eigentlich nichts besonderes. Wir erreichten den dazugehörigen Aussichtspunkt am Ende eines ereignisreichen Tages pünktlich zum Sonnenuntergang. Die Sonne selbst ist nicht zusehen, man kann aber erahnen, dass sie flach über dem Horizont steht. Stattdessen scheint der Himmel zu glühen und genau das macht die eigentliche Wirkung des Bildes aus und verhilft ihm zu seiner besonderen Lichtstimmung. Darüber hinaus erweckt es den Anschein, als würde hinter dem Betrachter gleich ein mächtiges Gewitter aufziehen (und tatsächlich hat dies dann auch den Versuch einer Langzeitbelichtung mittels ND-Filter vereitelt). Die EXIF-Daten bieten somit auch keine Überraschungen, seien an dieser Stelle aber der Vollständigkeit halber erwähnt: 27mm bei f/5.6, 1/100s und ISO200, fotografiert mit einer Canon EOS 6D samt Canon EF 24-70mm f/2.8 L. Nennenswerte Bearbeitung fand mit Ausnahme der künstlichen Vignettierung tatsächlich nicht statt.
Was war passiert?
Nun zum eigentlichen Aufhänger dieses Beitrags. Der Sachverhalt ist schnell zusammengefasst. Am 27. Januar dieses Jahres posteten wir auf unserem Instagram Profil das Bild wie folgt:
Auf keiner anderen Plattform hatten wir bis zu diesem Zeitpunkt das Bild irgendwie der Öffentlichkeit zugänglich gemacht. Noch am gleichen Tag erschien es dennoch auf der Facebook Seite der Great Ocean Road. Das Bild ist also von Instagram zu Facebook gewandert, und zwar dort auf eine tourismusmarketing-geprägte Seite, die einen zumindest ansatzweise kommerziellen Eindruck macht. Immerhin gibt es ein Impressum mit Adresse und Telefonnummer und jede Menge Posts, die ganz offensichtlich an zukünftige Besucher gerichtet sind. Zudem wurde das Bild in einen zwar nicht schlimmen, aber dennoch so nicht existenten Kontext gebracht ("Long weekend road tripping").
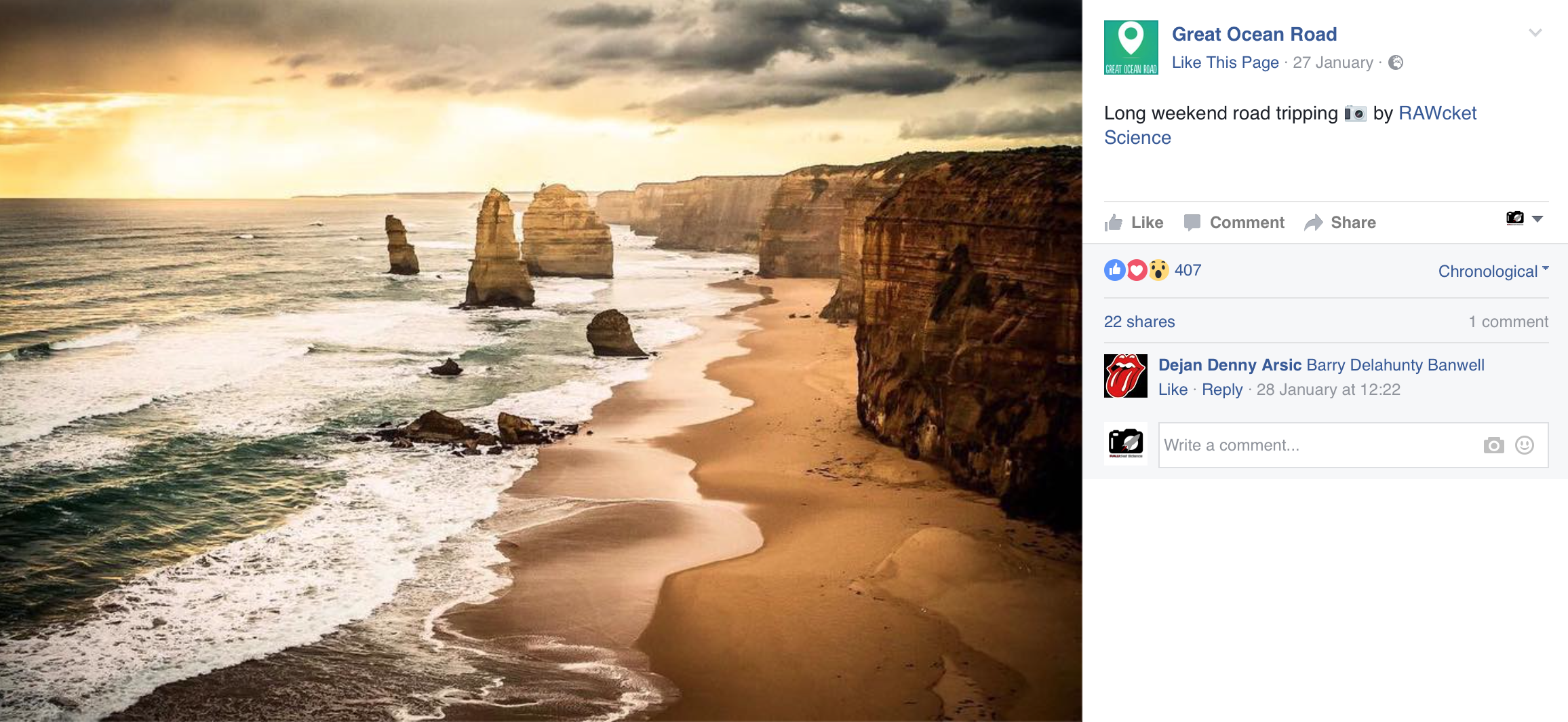
Unser Bild wurde also zumindest im weiteren Sinne kommerziell genutzt, ohne dass von uns irgendwelche Verwertungsrechte eingeräumt wurden. Natürlich kann man den konkreten Wert dieser Nutzung nur schwer bemessen und wir verdienen mit unseren Bildern auch nicht unseren Lebensunterhalt, können das also relativ entspannt sehen. Wir verkneifen uns erst recht eine urheberrechtliche Einordnung über Länder- und Kontinentgrenzen hinweg. Aber ein bisschen geht's hier einfach auch ums Prinzip! Wir würden vorher einfach gerne gefragt werden.
Wie kriegt man überhaupt mit, dass einem ein Bild geklaut wurde?
In unserem konkreten Fall wurden wir immerhin als Quelle verlinkt und haben so eine entsprechende Facebook-Notification bekommen. Das macht das ganze auch noch relativ erträglich. Gefragt werden würden wir trotzdem gerne (wurden wir auch schon, und haben nie nein gesagt). Und solange wir nicht von unseren Bildern leben müssen, werden wir eine Weiterverwendung vermutlich auch immer erlauben. Nicht zuletzt kann das der initiale Kontakt für eine Kooperation sein, die beiden Seiten was bringt!
Wenn man allerdings nicht durch Notifications aufgrund von Verlinkungen in sozialen Netzwerken automatisch benachrichtigt wird, muss man selbst aktiv werden. Das erfordert aber Zeit, die man unter Umständen nicht hat, erst recht, wenn das eigene öffentliche Portfolio sehr groß ist. Ein erster Ansatzpunt kann die Google Bildersuche sein. Ein Klick auf die kleine Kamera im Texteingabefeld erlaubt es einem dort nach konkreten Bildern (statt nach Worten) zu suchen. Mittlerweile gibt es aber auch diverse Webdienste, die sich auf die Aufdeckung von Bilderdiebstahl spezialisiert haben, zumeist aber kostenpflichtig sind. Da wir mangles Erfahrung keine Empfehlungen in dieser Hinsicht geben können, verweisen wir auf eine entsprechende Google Suche zum Thema. Zielgruppe dieser Dienste ist sicherlich in erster Linie auch eher der Berufsfotograf.
Was kann man dagegen tun?
Im Grunde nicht so viel, zumindest nichts, womit man sich nicht auch selbst ein Stück weit ins eigene Fleisch schneidet. Die folgenden Möglichkeiten bieten sich an:
- Da wäre zunächst das allseits beliebte Wasserzeichen. Auch wir machen davon regelmäßigen Gebrauch, allerdings weniger als Kopierschutz, sondern um einfach unsere Identität ein wenig mehr zu transportieren. Bei Wasserzeichen stellt sich immer die Frage, wie aufdringlich man sie gestaltet und platziert. Einerseits möchte man, dass sie den Bildeindruck nicht wesentlich verändern, andererseits aber schon, dass sie sie wahrgenommen werden. Man muss also das richtige Maß finden bei dem Gebrauch von Farben (insbesondere bei allem was nicht grau ist), Göße und Position. Je nach Motiv gilt es unter Umständen da individuell zu entscheiden. Beim folgenden Bild aus dem Elbsandsteingebirge haben wir zum ersten mal selbst reichlich Kritik (auf Facebook) für unser Wasserzeichen einstecken müssen, wurden im gleichen Atemzug aber für das Motiv selbst gelobt.
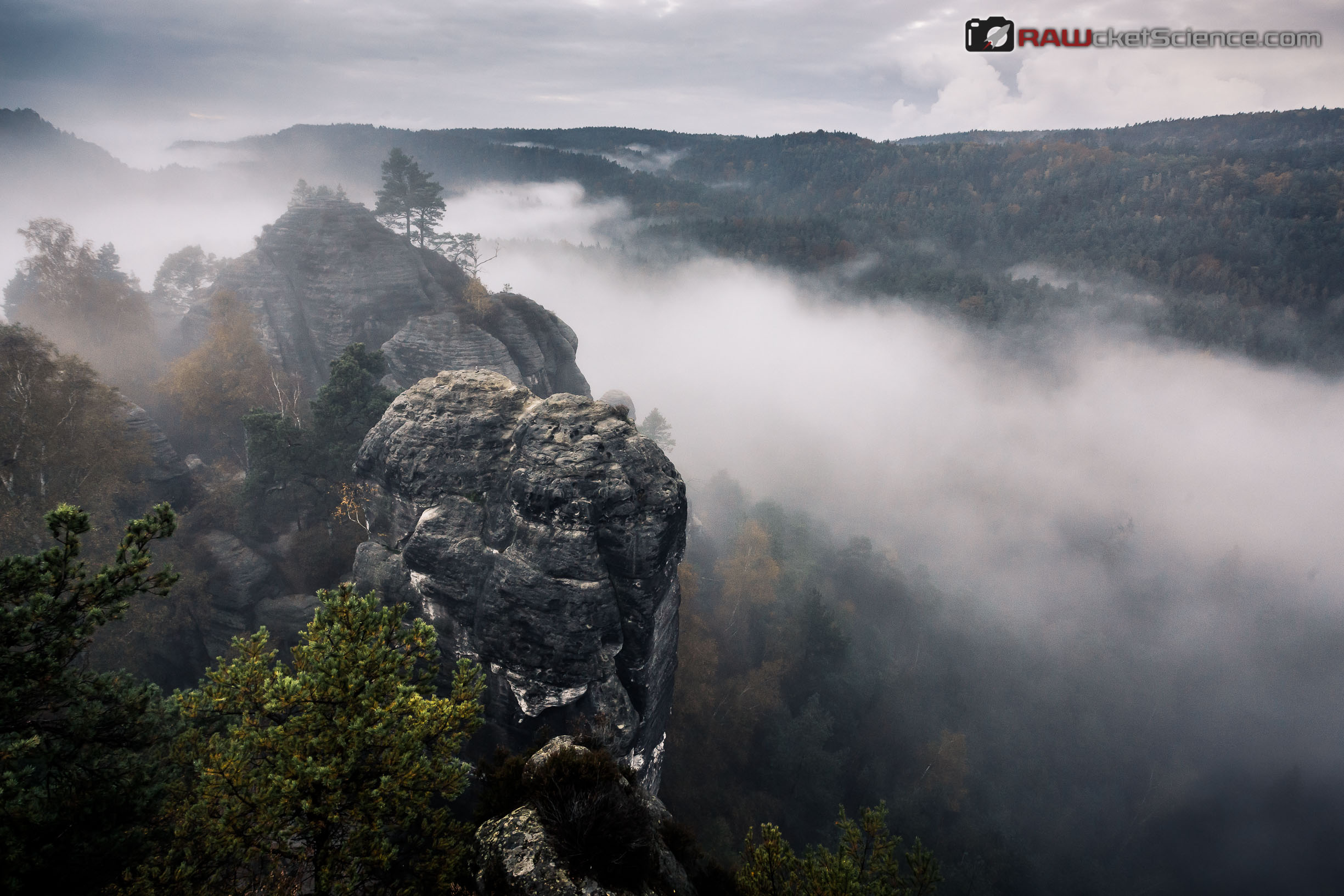 Im Nachhinein absolut nachvollziehbar. Da setzte einfach die mit der Zeit zunehmende Blindheit für das eigene Wasserzeichen ein. Ohnehin muss man sich eingestehen: verwendet man das Wasserzeichen als Kopierschutz, sollte man sich darüber im Klaren sein, dass wegstempelm und beschneiden sehr wirksame Gegenmaßnahmen sind, es sei denn, man plaziert sein Wasserzeichen mit einer gewissen Transparenz großflächig im Bild. Das wollen wir persönlich aber aus Gründen der Präsentationsqualität eher vermeiden.
Im Nachhinein absolut nachvollziehbar. Da setzte einfach die mit der Zeit zunehmende Blindheit für das eigene Wasserzeichen ein. Ohnehin muss man sich eingestehen: verwendet man das Wasserzeichen als Kopierschutz, sollte man sich darüber im Klaren sein, dass wegstempelm und beschneiden sehr wirksame Gegenmaßnahmen sind, es sei denn, man plaziert sein Wasserzeichen mit einer gewissen Transparenz großflächig im Bild. Das wollen wir persönlich aber aus Gründen der Präsentationsqualität eher vermeiden. - Außerdem kann man sich behelfen mit einer geringen Auflösung, die den Bilderklau unattraktiv macht. In der Zeit von hochaufgelösten Retina-Bildschirmen stößt das dem Betrachter aber wahrscheinlich auch sauer auf. Davon abgesehen ist einem vermutlich ja selbst daran gelegen, sein Bild in bestmöglicher Qualität zu zeigen, um den maximalen Eindruck zu erzielen. Ein Blick in die Hilfeseiten von Instagram verrät, dass unser Bild mit einer Bildbreite von maximal 1080 Pixeln geklaut worden sein kann. Das ist relativ wenig, aber auch noch nicht ausreichend störend im Format eines Facebook-Posts.
- Zu guter Letzt bleibt einem natürlich noch die Möglichkeit seine Inhalte durch Account Privatisierung zu schützen. Instagram Accounts können beispielsweise privat betrieben werden, so dass nur Follower die eigenen Bilder zu Gesicht bekommen können. Bei Facebook kann sie Sichtbarkeit eines Bildes auf den eigenen Freundeskreis beschränkt werden, etc... Davon abgesehen, dass auch das keinen 100%igen Schutz bietet, läuft es dem Ziel seine Bilder der breiten Öffentlichkeit zu präsentieren massiv zuwider, ist also auch nicht zielführend.
Fazit
Wie man sich selbst nun verhalten soll, muss man detailliert nach eigenen Interessen und konkretem Motiv entscheiden. Reichen passive Maßnahmen wie Wasserzeichen? Habe ich die Zeit aktiv nach meinen Bildern auf Seiten dritter zu suchen? Verdiene ich mit Bildern meinen Lebensunterhalt und bin deshalb von Reichweite abhängig? Bin ich tatsächlich bereit im Zweifelsfall rechtliche Schritte zu unternehmen? Das muss letztendlich jeder für sich selbst wissen. Eure Meinungen und Strategien würden uns allerdings stark interessieren! Wir freuen uns dementsprechend wie immer über Kommentare eurerseits (unter diesem Beitrag oder bei Facebook)!